Discover Jordan
1- Introduction
Jordan Is an Arab Muslim country, located in the north of the Arabian Peninsula and in West Asia. Bordered by Syria to the north, Iraq to the east, Saudi Arabia to the south and south-east, and Palestine (the West Bank) to the west.
Although Jordan is a young state, Jordan’s inhabitants witnessed many civilizations over the last five thousand years. Part of the Ottoman Empire until 1918 and later a mandate of the United Kingdom, Jordan has been an independent kingdom since 1946.
The capital and largest city in the country is Amman, is one of the region’s key commercial and transportation centers as well as one of the Arab world’s major cultural capitals.

2- Geography
Jordan shares a 1,635 km border with Saudi Arabia, 375 km with Syria, and 181 km with Iraq. The highest point stands at 1854 m on the summit of Mount Umm Al-Dami.
3- Regions
Jordan has three major geographical regions:
· The desert region (from east to west, 4/5 of total area) is an extension of the Arabian Desert and occupies the eastern and southern parts of the country.
· The uplands east of the Jordan River, an escarpment overlooking the rift valley, have an average elevation of 2,000–3,000 feet (600–900 meters) and rise to about 1854 meter on Mount Umm Al-Dami in the south.
· The Jordan Valley (the northwest portion of the great East African Rift System) drops to about 408 meters below sea level at the Dead Sea, the lowest natural point on Earth’s surface.
From an administrative dimension, Jordan is divided into 12 Governorates falling under three regions:
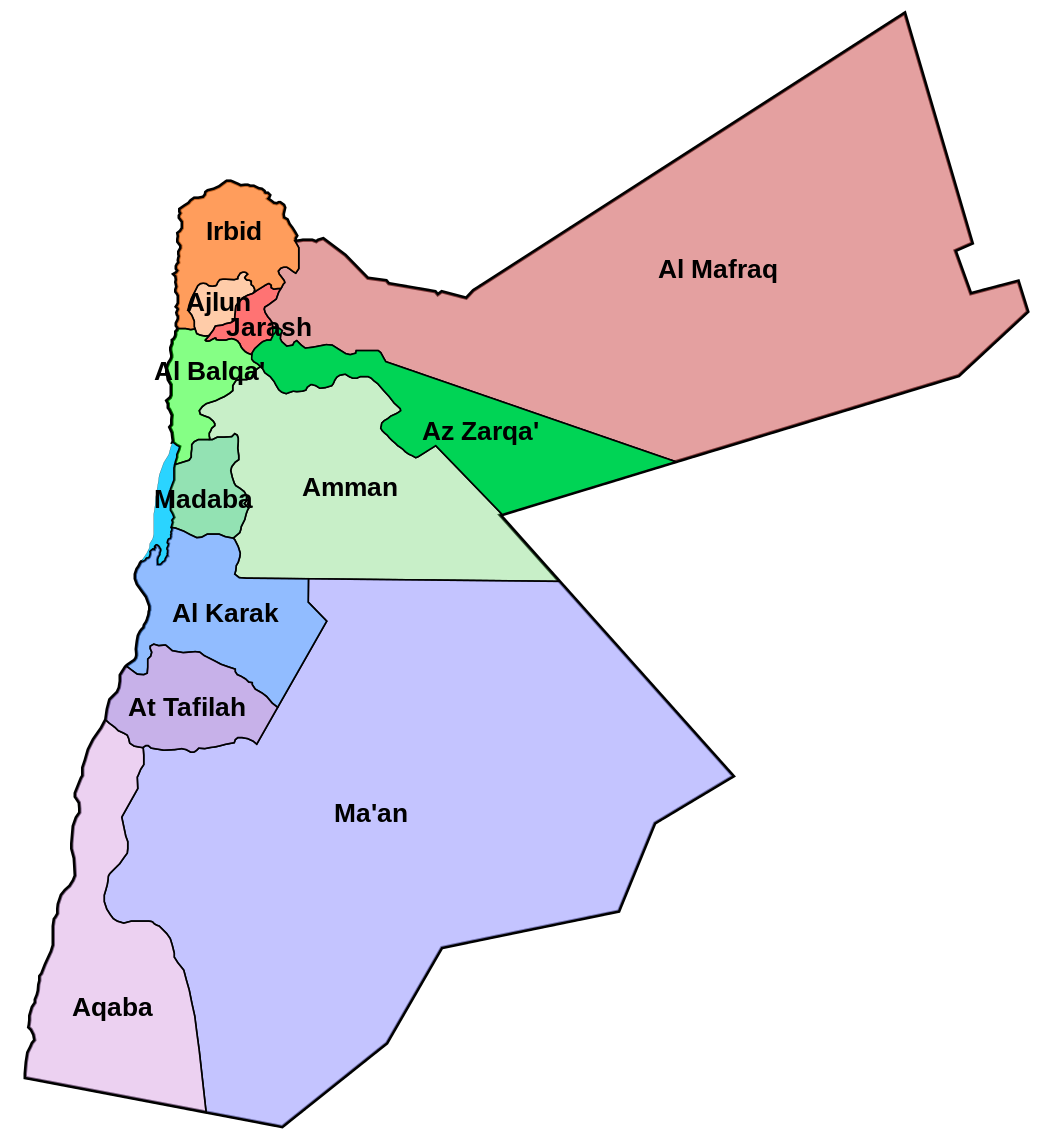
| Governorate | Area (km2) | |
| 1 | Irbid | 1,572 |
| 2 | Ajloun | 420 |
| 3 | Jerash | 410 |
| 4 | Mafraq | 26,551 |
| North Region: total | 28,953 | |
| 5 | Balqa | 1,120 |
| 6 | Amman | 7,579 |
| 7 | Zarqa | 4,761 |
| 8 | Madaba | 940 |
| Central Region: total | 14,400 | |
| 9 | Karak | 3,495 |
| 10 | Tafilah | 2,209 |
| 11 | Ma'an | 32,832 |
| 12 | Aqaba | 6,905 |
| South Region: total | 45,441 | |
| Jordan: total | 88,794 | |
5- Climate
The country is mainly dry, with temperatures at the capital ranging from 8 to 26 °C, whereas at in the southern city of Aqaba, ranging from 60 to 91 °F (16 to 33 °C).
6- People
Population & Ethnic groups
According to recent estimates, Jordan population is 11 million people (2022). Arabs make up the vast bulk of the population, namely Jordanians and Palestinians. A sizable number of Syrian refugees who came to Jordan due to the Syrian Civil War, as well as Iraqis who fled to Jordan as a result of the Persian Gulf War and the Iraq War, are examples of other minorities.
7- Language
The official language of the nation is Arabic, which is spoken by all Jordanians. Different dialects are used, but they are all mutually understandable and resemble the Levantine Arabic used in some areas of Palestine, Lebanon, and Syria.
8- Religion
The official religion is Islam, with Sunni Muslims comprising the majority of population (92%). The Christian (6%) of the population, most of which follow the Orthodox Church.
9- Demographic trends
Internal migration from rural to urban centers has increased over the last 25 years. The population structure is predominantly young; persons under age 16 constitute more than one-third of the population.
10- Economy
Diversified Economy
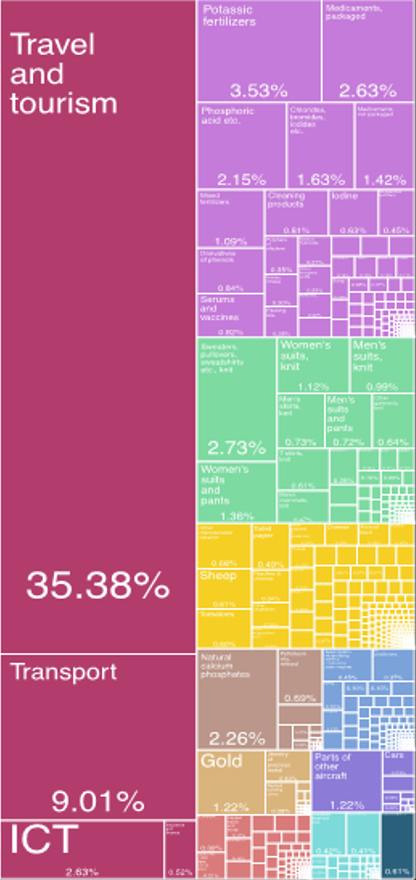
Jordan's economy is a diversified economy, with strong contribution from trade, finance, Industry, and services. In 1999 the government began introducing number of economic reforms. Top sectors in terms of contribution to GDP is services (around two thirds), industry (less than one third), and Agriculture.
Jordan is an upper-middle-income country. It’s one of the most open and diversified economies in the Arab world:
· No. 93 economy in the world in GDP
· No. 113 economy in GDP per capita
· No. 91 in total exports
· No. 81 in total imports
· No. 67 most complex economy according to the Economic Complexity Index (ECI)
· Jordan’s Global Competitiveness Index increased from 59.17 to 60.94 (Global Economic Forum, 2017-2019).
· Jordan increased by 7.7% its Doing Business Score (World Bank, 2020).
· The Global Entrepreneurship Index improved 23 positions between 2014 and 2018 (from 72 to 49).
· Jordan outperforms the region in product innovation, technology absorption, competitiveness, and startup skills.
· The most important sector is Services, followed by Manufacturing and Mining.
11- Business Sectors
The business environment in Jordan is envisioning new horizons after the Covid pandemic. To stimulate its business environment and meet challenges, Jordan is improving education and health services, modernizing its infrastructure, addressing structural problems, and focusing its strategy on increasing and expanding exports to current and new markets.
· Jordan was the first Arab country in the Middle East to adopt competition legislation in 2002.
· Financial services have been opened to foreign competition.
· Since 1985, the Investment Promotion Law has offered opportunities to foreign investors.
· Jordan has established several locations for investment promotion: industrial estates, development areas, free zones, and the Aqaba Special Economic Zone (ASEZ), with its regulatory framework and incentive system.
· Trade and finance correspond to almost one-third of the country’s GDP.
· Transportation and communication, public utilities, and construction correspond to one-fifth of the country’s GDP.
· Mining and manufacturing correspond to one-fourth of the country’s GDP.
· Tourism, including medical, is a vital sector recovering from the global pandemic impact.
· Jordan ICT’s sector holds the leading position in the MENA region with a modern world-class ICT infrastructure
.· Telecommunications provide reliable and redundant international connectivity.
12- Agriculture
Key exported Agricultural products included Tomatoes, Bell Pepper, Lettuce, Peach, and Watermelon. Key export markets are Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, UAE & Bahrain.
13- Resources and power
Jordan has large amounts of phosphates and potash and considered a leading global producer and exporter. Thermal power stations, the most of which are oil-fired, produce the majority of the electricity in Jordan. A transmission system links the major power plants.
14- Manufacturing
Majority of manufacturing activities are based close to Amman. Extractive industries are growing in terms of contribution to exports. Other activities include Food, clothing, and consumer goods.
15- Finance
The Central Bank of Jordan issues the dinar, the national currency. The central bank also regulates the banking sector that includes over 20 local and international banks active in Jordan.
16- Tourism
Since the middle of the 1990s, Jordan has seen a sharp increase in the number of tourists visiting. Jordan is working hard to close its balance-of-payments deficit, and tourist revenue is a key component of this endeavor.
Tourism is one of the leading and diverse exports in Jordan's services-oriented economy. After an upward trend since 2005, tourism international receipts, as a percent of total exports, reached a peak of 42% in 2019. However, in 2020, the year of COVID-19 emergence, tourism receipts sharply declined to 17% of total exports, compared to 7% for Turkey, and 12% for both Morocco and Egypt. These Jordanian tourism figures include tourism income from Jordanian residing abroad.
For information, please check following page on the portal: Tourism in Jordan
Jordan is a member of the World Trade Organization (WTO). The country has signed a considerable number of trade agreements which is corresponding with its open economic approach. Jordan has pursued a trade liberalization strategy at regional, bilateral, and multilateral levels in recent years.
The export sector is a priority for its employment potential. Jordan is investing heavily in modernizing, increasing competitiveness, and increasing exports. It’s estimated that Jordan could create more than 85,000 new jobs (with 25% of new jobs for women) just by unlocking its export potential in the region (Turning export potential into employment: A case study for Jordan, ITC, 2018).
· Jordan has modernized customs procedures and a risk-based inspection system.
· Goods and services account for 56% and 44% of exports, respectively.
· Total exports in goods reached 2.147 billion JOD (Jan-May 2021).
· Jordan is experiencing a 22.3% exports growth YOY (Jan-May 2021).
· During the first half of 2021, Jordan has exported to 147 countries.
· Top exports apparel and textiles, fertilizers, inorganic chemicals, organic or inorganic compounds of precious metals, rare-earth metals, and pharmaceuticals.
· Top countries served by Jordan: USA, India, Saudi Arabia, Iraq, and the United Arab Emirates.
· Top sectors for export investments: meat and poultry products, Dead Sea products, and apparel and textiles.
To know more, check out Jordan Exports’ website solutions & services, intelligence & insights, and projects & initiatives.
Jordan's main exports are clothing, chemicals, and potash; its main imports are machinery and apparatus, crude petroleum, and food products. Major destinations for exports are the United States, Iraq, and Saudi Arabia; major sources of imports are Saudi Arabia, the U.S., China, and the EU.
Jordan is an open economy, with a wide network of bilateral, regional and multilateral trade agreements, including with North America (the United States and Canada) and the European Union (EU).
Further, Jordan acceded to the World Trade Organization (WTO) in the year 2000. As a result, Jordan’s total foreign trade (merchandise total exports plus imports) reached 69% of GDP (2021 figure). According to UNCTAD, Jordan enjoys a respectable score of 0.81 for export performance index in Q4 2021, compared to 0.42 for Morocco, 0.47 for Tunisia and 0.73 for UAE. Export performance index is a composite indicator which includes export growth of goods and services; performance vs. peers (export performance of direct competitors); as well as export diversification and competitiveness in major and dynamic markets. A greater score implies higher export performance. With improved global competitiveness and export readiness, Jordan's diverse trade network would enable Jordanian companies to have better market access to key world markets.
For information, please check following page on the portal:Trade with Jordan
18- Services
Services are the single most significant sector of Jordan's economy in terms of both value and employment, including public administration, defense, and retail sales.
19- Health Care
According to the World Bank, Jordan offers the best health care services in the Middle East.
Between 2012 and 2016 alone, the Jordanian public health facilities assisted around 1.8 million Syrian refugees.
20- Technology & IT
Jordan has become a center for technology start-ups in the Middle East and is home to annumber of ICT businesses. The fixed-line service monopoly was broken in 2005, and the entire telecoms industry was made competitive. The digital economy, a thriving mobile industry, and a sizable LTE infrastructure are essential to the government's economic objectives.
In 2019, Ministry of Digital Economy & Entrepreneurship (MoDEE) has replaced the Ministry of Information and Communication Technology (MoICT). The name was changed to reflect the role of the ministry leading the country and its ICT industry as it incorporates the wider digital and becomes more invested in entrepreneurship.

