E-commerce presents an important opportunity to address some of the major challenges faced by the Jordanian economy and to become a driver of sustainable economic growth. A consumer survey conducted by the market research company Statista found substantial increases in the use of e-commerce among Arab countries, with a third of the respondents from Jordan saying that they have been shopping online more frequently.
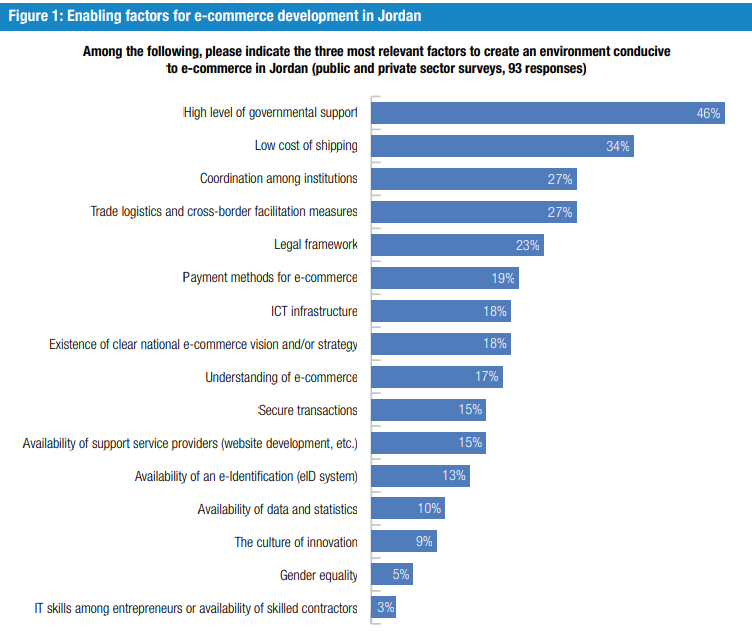
While the full potential of e-commerce remains untapped, there are three major factors that could spur digital growth in Jordan: its tech-savvy young population, the relatively well-developed ICT and innovation sectors, and the strategic position of Jordan between the East and the West. Jordan also benefits from a mature business environment with regard to digital companies and startups, financing institutions, incubators, accelerators, and other mechanisms supported by a myriad of local and international partners. This is another positive factor for the development of e-commerce in the country, provided that high-level governmental support translates into enhanced coordination among all stakeholders, including development partners, and continuous improvement of the quality of services provided along the entire e-commerce value chain.
The state of e-commerce in Jordan is considered relatively advanced, having a medium readiness on the UNCTAD B2C E-commerce Index. A national e-commerce strategy was adopted already in 2008 but was not fully implemented. The overall e-commerce ecosystem in the country at the time, the dedicated human and financial resources, and the necessary implementation mechanisms were not adequate for its implementation. Unlike 10 years ago, at present Jordan seems to be in a better position to create a conducive environment for a thriving e-commerce. National plans and policies are calling for the development of a strategic roadmap to promote e-commerce in the country, to boost online and trade activities and make it an effective tool to enable export growth.
ICT infrastructure and services
Jordan has been a pioneer in the development of a highly competitive ICT sector in the MENA region. ICTs have been an engine of growth for the national economy in general and e-commerce. In recent years the sector has experienced exponential growth, in large part due to support from the highest political level and a long-standing enabling environment. Both fixed and mobile communications are liberalized with multiple service providers. 3G and 4G networks are available, and a 5G network is expected to be available by 2023. However, there are significant inequalities between urban and rural areas regarding Internet and mobile connectivity, which have an adverse impact on the establishment and growth of start-ups outside major cities. In addition, the cost of the Internet remains high, and users across the country often experience bandwidth and connectivity issues.

Trade logistics and trade facilitation
Trade facilitation and delivery costs are key factors for creating an environment conducive to e-commerce. In Jordan, however, the capacity of local delivery service providers is insufficient. The time needed for the last mile delivery frequently exceeds the time for international delivery. High national and international delivery costs pose challenges to e-commerce development. The postal system consists of a public postal operator and several private postal operators with local and international licenses. The quality and efficiency of the latter, however, exceed those provided by the Jordan Post Company. With regard to trade facilitation, Jordan performs well on international rankings, but improvements are necessary in the area of cross-border trade. The physical addressing system is only partially implemented. However, service providers have been able to circumnavigate this problem by using technology-based solutions
Payment solutions
While Jordanian businesses and consumers prefer traditional in-cash payment methods, the Central Bank of Jordan and other actors have exerted efforts to shift towards electronic payments, and noticeable progress has been achieved in this regard. The Central Bank operates several retail payment systems allowing electronic payments. The regulatory framework supports the development of the financial sector and electronic payments. Major reforms were introduced over the past couple of years to govern and improve various aspects of financial transactions. Since the outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic, the Central Bank of Jordan has implemented a series of measures to protect the economy and society from its impact, which resulted in a sizeable increase in electronic transactions in 2020. The number and use of e-Wallets are also growing exponentially. Nonetheless, the vast majority of SMEs have not adopted e-payment solutions.

Legal and Regulatory Frameworks
The current Jordanian legal and regulatory frameworks do not offer the necessary provisions to support the development of e-commerce through adequate protection of SMEs and consumers. While a number of laws have been drafted and promulgated, they are incomplete or partially implemented, do not align with regional and international best practices, and do not adequately address the specific needs of e-commerce and the digital economy. Some laws – such as with regard to data and privacy protection – are absent. Most SMEs in Jordan are also not aware of the existing laws and regulations and how they protect their interest concerning electronic transactions.

E-commerce skills development
While Jordan is a regional leader in the modernization and development of its educational system, university graduates still lack the skills and talents required by e-commerce and the digital economy. There is a high and increasing demand for e-commerce programs. Currently, Jordanian universities introduced new e-commerce and tech-based programs. Public and private sector stakeholders and development partners are implementing numerous initiatives to build the capacities of both SMEs and graduates to develop their digital skills. However, these efforts are not well coordinated, which leads to sub-optimal results in the acceleration of Jordan’s transition into a digital economy.
Overall, business growth has been slow and limited, and the SME ecosystem is still in an early stage of development. The public sector also lacks the necessary skills and knowledge for seizing the benefits of e-commerce and for building an enabling environment for online trade
Access to financing
The Central Bank of Jordan has introduced many reforms and policies to improve access to credit and financial opportunities for all segments of the population. Nevertheless, loans from licensed banks do not serve the needs of entrepreneurs and SMEs. In particular, the interest rates offered by banks are too high for entrepreneurs, despite the reduced interest rates provided by the Central Bank. Furthermore, banks’ requirements for collateral prevent entrepreneurs especially youth, women, and other vulnerable groups – from accessing financing opportunities. The financing market also offers limited opportunities for access to venture capital. While initiatives to financially support SMEs exist, entrepreneurs are not always aware of their existence. SMEs also lack the knowledge of how to evaluate their funding needs, especially regarding e-commerce, which is a relatively new field. This lack of awareness reduces the likelihood of companies applying for financing. Overall, the financing system currently does not provide the support that startups need to establish, grow, and engage in e-commerce. Similarly, access to finance remains a major challenge for women. Female participation in startups has increased, demonstrating their potential contribution to the development of e-commerce, provided that digital and financial literacy are further improved.